When we think of fruits, a rainbow comes to mind—reds, yellows, oranges, greens, and deep purples. But one shade almost never seen in nature is teal, the enchanting blue-green tone that evokes oceans, gemstones, and lush tropical jungles. While true teal fruits are extremely rare, nature does offer a few fruits with bluish, greenish-blue, or teal-tinted characteristics. Beyond the real, teal fruits have also become popular in food art, culinary creativity, and even fictional or conceptual design.
click in link Strawberry Shortage
What Makes Teal So Rare in Fruits?
Color in fruits depends on pigments—primarily anthocyanins, carotenoids, and chlorophyll.
- Carotenoids produce warm colors like yellow, orange, and red.
- Chlorophyll creates shades of green.
- Anthocyanins produce blues, purples, and reds.
To achieve a true teal shade, a fruit would need a complex balance of pigments, particularly anthocyanins mixed with yellow or green tones. However, this delicate combination rarely occurs naturally, which is why teal fruits are nearly nonexistent. Even fruits that appear blue often lean toward purple or indigo.
That makes the few naturally bluish-green fruits even more fascinating.
1. Fruits That Come Close to Teal in Nature
Although not perfectly teal, several fruits come close enough to inspire curiosity.
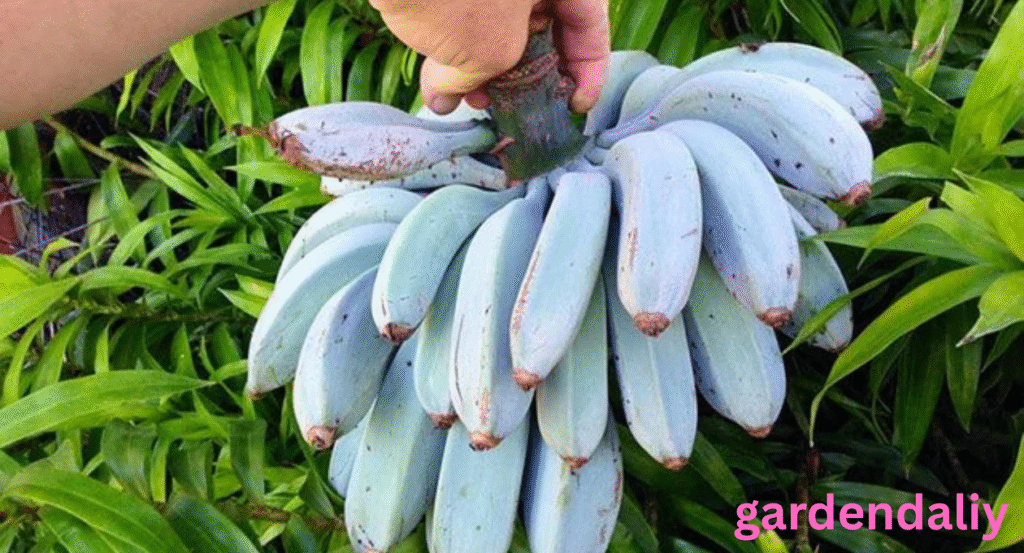
Blue Java Bananas (Ice Cream Bananas)
These bananas are famous for their bluish-silver peel, which can sometimes resemble a soft teal hue before ripening. Inside, they offer a creamy texture and vanilla-like flavor, making them a favorite among fruit enthusiasts.

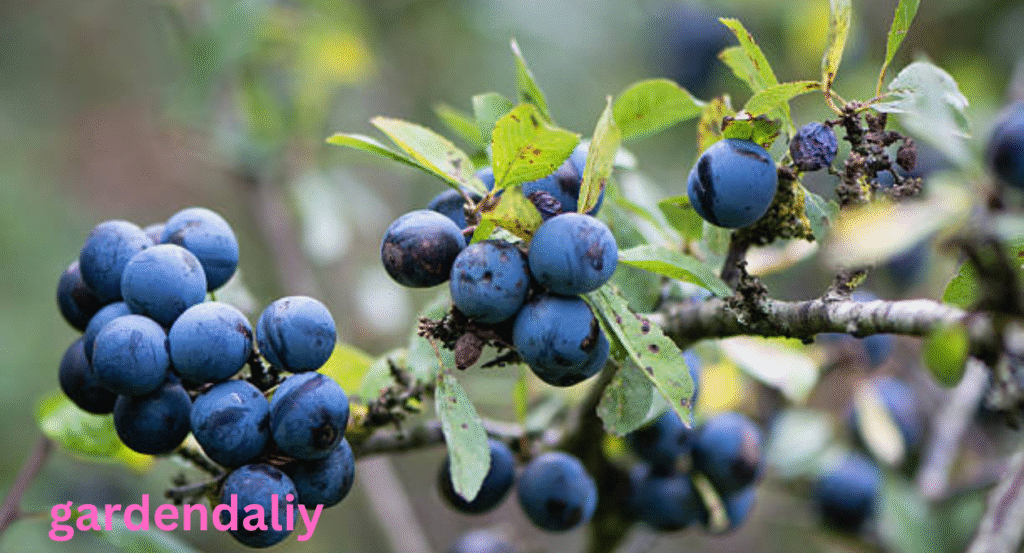
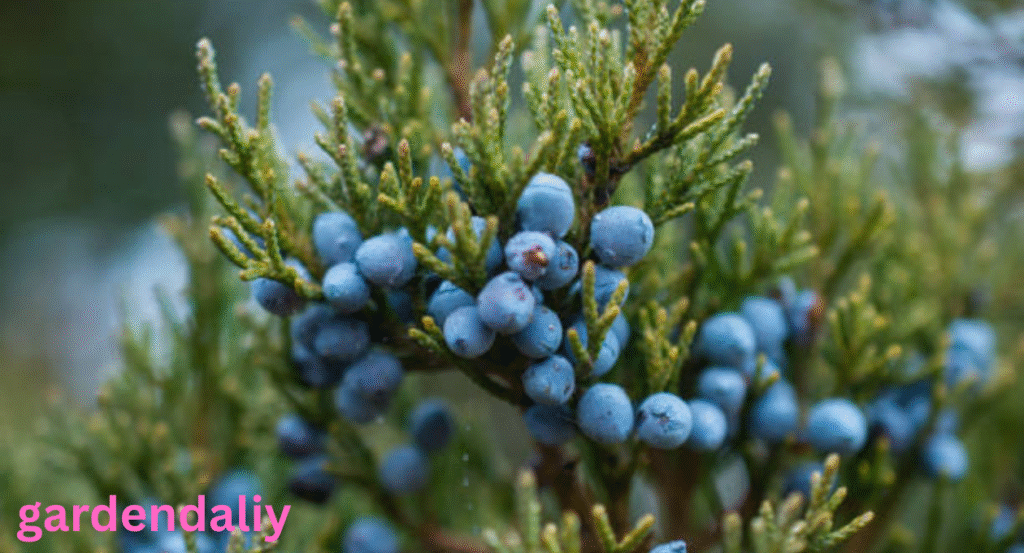
Juniper Berries
Juniper berries often appear deep bluish-green, especially when light reflects off their waxy surface. While not typically eaten like regular fruit, they are widely used for flavoring, including in the production of gin.

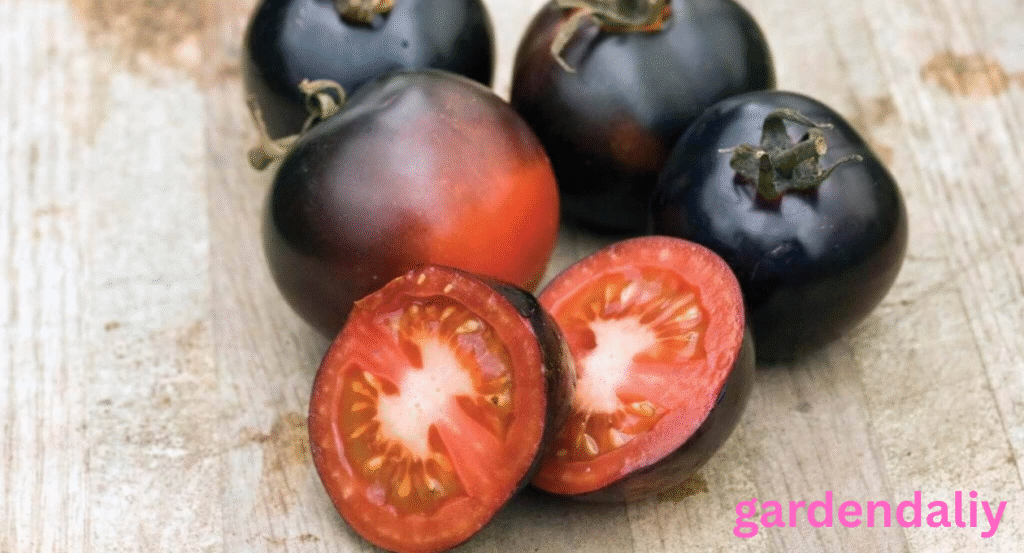
Indigo Rose Tomatoes
While mostly deep purple, some varieties take on a smoky bluish tint when exposed to sunlight. The combination of green and purple pigments can occasionally create a teal-like effect around the shoulders.

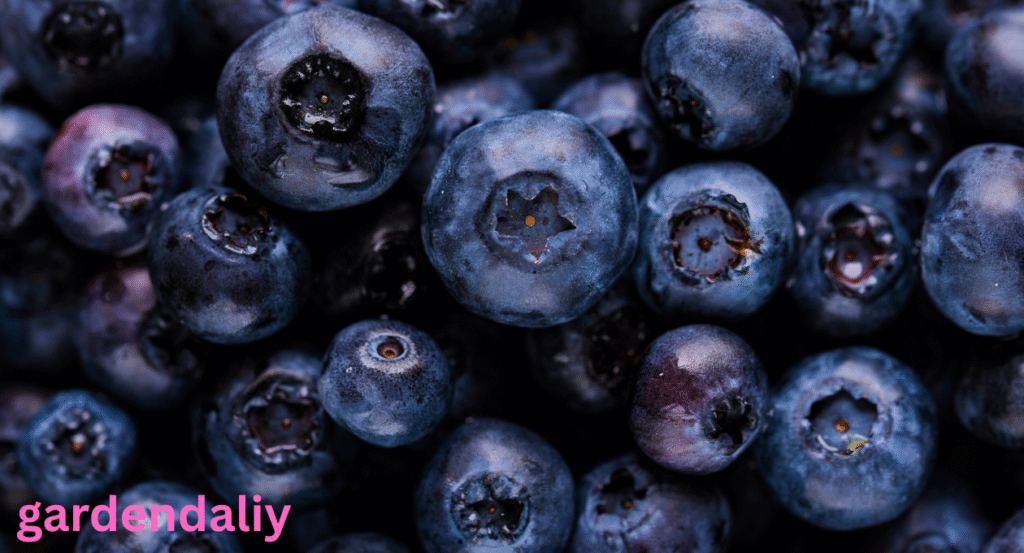
Blueberries
Though primarily blue-purple, some berries—especially when coated with their natural waxy “bloom”—can appear slightly greenish-blue, producing a tone close to teal.
These fruits remind us that nature’s palette, though limited, contains surprising variations when conditions align.

2. The Rise of Teal Fruits in Culinary Art
Because nature rarely produces teal fruit, chefs, designers, and home cooks have embraced the challenge creatively.
Teal-Themed Platters and Desserts
Food stylists have begun using natural dyes like butterfly pea flower—which produces a stunning blue that can shift toward teal when mixed with citrus—to create:
- Teal fruit jellies
- Teal smoothie bowls
- Teal-coated berries
- Teal-glazed fruit tarts
These dishes blend real fruits with artistic coloration, appealing to social media aesthetics and themed events.
Artificial and Conceptual Teal Fruits
In digital art and culinary design, teal fruits have become symbols of futurism and fantasy. They appear in:
- Book illustrations
- Video game graphics
- Sci-fi worldbuilding
- Fictional ecosystems
These imagined teal fruits often represent magical properties or alien origins.
3. Why People Are Drawn to Teal Fruits
The color teal is associated with calmness, creativity, and mystery. In food, it evokes a sense of novelty and elegance. People are naturally drawn to things that challenge expectations, and teal fruits do exactly that.
Symbolism of the Color Teal
- Balance: A blend of tranquil blue and refreshing green
- Uniqueness: Rare in both nature and cuisine
- Modernity: Popular in graphic design and branding
This emotional appeal makes teal fruits—real or imagined—especially attractive.
4. Can We Grow Teal Fruits in the Future?
Science is already manipulating pigments in plants to create new colors. Through selective breeding, hybridization, and even genetic editing, researchers can adjust anthocyanin and chlorophyll levels to produce new hues.
Future possibilities include:
- Nutrient-enhanced blue-green berries
- Teal-toned tropical fruits
- Health-focused produce combining natural blue antioxidants with green nutrients
While ethical and environmental considerations remain important, the idea of teal fruits entering supermarkets one day is not impossible.
5. How to Create Teal Fruit Dishes at Home
Even if nature doesn’t provide teal fruits, you can bring the aesthetic to your kitchen.
Use Natural Colorants
- Butterfly pea powder + lemon juice → bright teal
- Spirulina → deep blue-green tones
- Matcha + blue spirulina → layered teal effects
Creative Serving Ideas
- Teal smoothie bowls topped with kiwi, banana, and berries
- Fruit popsicles tinged with natural blue-green color
- Teal-drizzled fruit salad for parties or events
These creations maintain fruit’s natural taste while adding exciting color.
Conclusion
While teal fruits are rare in the natural world, their allure is undeniable. Whether found in the slight bluish-green sheen of a juniper berry or crafted through artistic culinary design, teal fruits capture the imagination. They represent innovation, curiosity, and the desire to explore beyond traditional boundaries.
click in link Strawberry Shortage
Teal fruits remind us that nature still holds mysteries—and creativity lets us expand those wonders even further.
faqs
1. Do teal fruits exist naturally?
True teal fruits are extremely rare in nature. However, some fruits—like Blue Java bananas, juniper berries, and certain tomatoes—can show bluish-green or teal-like tones due to unique pigment combinations.
2. Why are teal fruits so uncommon?
Fruit color comes from pigments like chlorophyll, anthocyanins, and carotenoids. To produce teal, a fruit would need an unusual balance of blue and green pigments. This combination almost never occurs naturally.
3. What fruits come closest to teal?
Fruits with tones close to teal include:
- Blue Java (ice cream) bananas
- Juniper berries
- Indigo Rose tomatoes
- Some blueberries with a waxy coating
Though not perfectly teal, they offer blue-green hues.
4. Can teal fruits be created artificially?
Yes. Culinary artists often use natural food colorants like butterfly pea flower, spirulina, or matcha blended with blue dyes to create teal-colored fruit dishes, smoothies, and desserts.
5. Are teal fruits safe to eat?
Naturally occurring fruits with bluish-green tones are safe if eaten ripe. Artificial teal foods using natural colorants (butterfly pea, spirulina) are also safe. However, brightly colored synthetic dyes should be consumed in moderation.